Why Use an Isolated Driver in Your LED Light?
In the world of LED lighting, the LED driver plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and longevity of LED lights. With the increasing popularity of LED fixtures and the growing demand for energy-efficient lighting solutions, it’s essential to understand the difference between isolated and non-isolated LED drivers. In this article, we will explore the safety and lifecycle aspects of isolated drivers and delve into the advantages and considerations associated with them.
The Importance of Safety in LED Drivers
Safety is a paramount concern when it comes to LED lighting. Isolated LED drivers provide an extra layer of protection due to their design. They feature a transformer and an optocoupler that isolate the primary and secondary sides of the driver, ensuring that any abnormal situations on the primary side do not directly affect the secondary side. This isolation mechanism significantly reduces the risk of electric shock for users and installers, making isolated LED drivers a safer choice overall.
On the other hand, non-isolated LED drivers rely on the insulation and safety assessments conducted by luminaire manufacturers. While the non-isolated LED driver itself may not be inherently safe, luminaire manufacturers can enhance the insulation of the fixture to mitigate the risk of electric shock. However, it’s important to note that even with safety regulations, non-isolated LED drivers do not guarantee absolute safety. Careful consideration of users’ conditions and compatibility with LED drivers is crucial when designing LED Lights to minimize the risk of electrical hazards.
Lifespan Comparison between Isolated and Non-isolated LED Drivers
The lifecycle of LED drivers is a key factor to consider when selecting the right driver for your LED lighting applications. While it’s challenging to precisely analyze the difference in lifecycle between isolated and non-isolated LED drivers, various factors come into play.
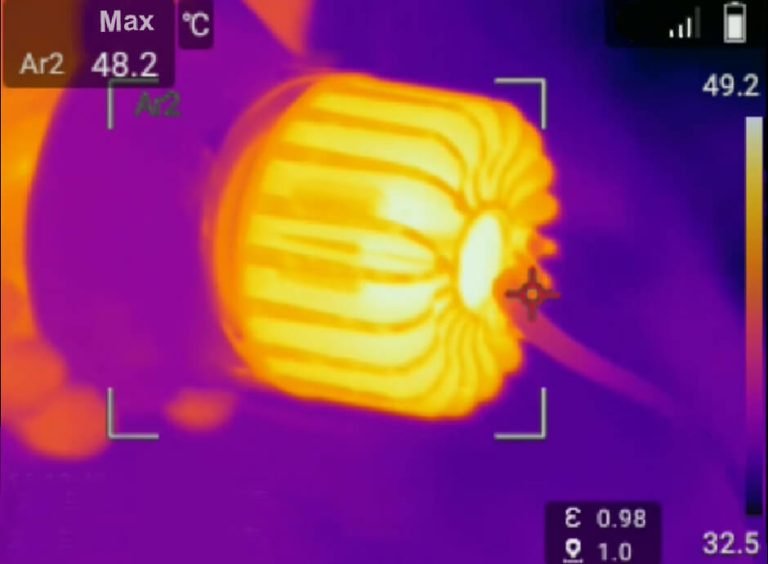
Isolated LED drivers tend to have a longer average lifespan due to their design and surge tolerance capabilities. The transformer in isolated drivers prevents surge voltages from flowing to the secondary side, protecting the LED from potential damage. In contrast, non-isolated LED drivers lack transformer isolation, making them more susceptible to surges. If surge issues are not adequately addressed, the LED may face the surge directly, leading to a shorter lifecycle compared to isolated LED drivers.
It’s worth noting that non-isolated LED drivers are often used in highly competitive markets with lower power and price requirements. As a result, these drivers are often designed for shorter lifecycles and may not offer the same longevity as their isolated counterparts.


MEAN WELL's Approach to Isolated LED Drivers
MeanWell drivers have a large share of the LED lighting segment. While non-isolated LED drivers may have advantages in terms of cost and efficiency, MeanWell chooses to focus on providing high-cost performance and isolated LED drivers. MEAN WELL’s latest new products, such as the XLG, XBG, and SLD series, exemplify this commitment.
MEAN WELL acknowledges that safety and lifecycle issues need to be thoroughly addressed before venturing into non-isolated LED driver manufacturing. Rather than engaging in a price war, MEAN WELL continues to invest in innovative products and industries, ensuring that customers receive reliable, high-quality LED drivers that adhere to the strictest safety standards.
We are able to obtain competitively priced products from the first tier distributors. Please contact us(Email:sales@top-lamps.com)if you need any drivers of MeanWell.
Advantages of Isolated LED Drivers
Isolated LED drivers offer several advantages that make them a preferred choice for many lighting applications. Let’s explore some of these benefits:
Enhanced Safety
The primary advantage of isolated LED drivers is their superior safety features. The isolation between the primary and secondary sides prevents high voltage from flowing directly to the secondary side, ensuring the safety of users and installers.
Lower Risk of Electrical Hazards
Isolated LED drivers significantly reduce the risk of electrical hazards, such as electric shock. LED panel lights, for example, are the most common lighting application, used in hospitals, schools or public places. These places have very high safety requirements and should use isolated drivers.
Greater Surge Protection
The transformer in isolated LED drivers provides surge protection, safeguarding the LED from voltage spikes and transient events. This increased surge tolerance enhances the lifespan of the LED and reduces the risk of premature failure.
Flexibility in Design
Isolated LED drivers offer more flexibility in luminaire design. The isolation allows for different dimming options, such as 0-10V or DALI, without compromising safety or causing compatibility issues.
Reliability and Longevity
With their robust design and enhanced surge protection, isolated LED drivers tend to have a longer lifespan compared to non-isolated drivers. This reliability translates into reduced maintenance costs and improved overall performance of LED lamp.
Considerations for Isolated LED Drivers
While isolated LED drivers offer numerous advantages, it’s essential to consider certain factors before incorporating them into your lighting projects. Here are some key considerations:
Driver Cost
Isolated LED drivers generally have a higher upfront cost compared to non-isolated drivers due to the additional components required for isolation. However, their longer lifespan and enhanced safety features can offset this initial investment over time.
Space and Size
Isolated LED drivers may occupy more physical space due to the inclusion of a transformer and other isolation components. This factor should be considered when designing luminaires with space constraints.
Efficiency
In some cases, isolated LED drivers may have slightly lower efficiency compared to non-isolated drivers. However, advancements in technology and design have minimized this efficiency gap, making isolated drivers a viable option for energy-efficient lighting solutions.
Choosing the Right LED Driver for Your light
When it comes to selecting the right LED driver for your lighting application, it’s essential to evaluate your specific requirements and consider the advantages and considerations of both isolated and non-isolated drivers. Here are some key factors to keep in mind:
Driver Safety
If safety is a top priority, especially in environments with strict regulations or sensitive applications, an isolated LED driver would be the recommended choice.
Budget Constraints
If your project has tight budget constraints and cost-effectiveness is a primary concern, a non-isolated LED driver can offer an economical solution without compromising essential safety features.
Driver Longevity
If longevity and reliability are critical factors, particularly in applications where maintenance is challenging, an isolated LED driver’s enhanced surge protection and longer lifespan make it the preferable choice.
Efficiency Requirements
Consider the desired energy efficiency levels for your lighting project. Both isolated and non-isolated LED drivers can achieve high levels of efficiency, but specific design considerations may affect overall performance.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding the difference between isolated and non-isolated LED drivers is crucial when selecting the right driver for your LED lighting projects. Isolated LED drivers offer enhanced safety features, surge protection, and longer lifespan, making them an ideal choice for applications where safety and longevity are paramount.